- Select Language
The T80 handheld PDA combines advanced barcode sca...
Explore an innovative Personal Digital Assistant f...
AR smart glasses merge digital content with the real world, allowing users to see street navigation arrows, view real-time translations, or access work instructions hands-free. What makes these compact devices so powerful? This article will analyze the key technologies behind AR smart glasses, from the display system to sensors, processing chips, and interaction methods.

AR Display Technology
At the heart of any AR smart glasses is the display system, which projects digital images into the wearer's field of view without obstructing the real world.
Waveguide Display
How it works: Light from a microdisplay passes through a transparent lens and shines directly into the eye.
Advantages: Lightweight and thin lenses suitable for everyday wear, like glasses.
Examples: hotus AR smart glasses
Micro-OLED and LCoS Panels
Micro-OLED: Provides ultra-high contrast and vibrant colors, ideal for media consumption.
LCoS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon): Provides high brightness, suitable for outdoor AR applications.
Use Cases: AR navigation and video streaming.
Projection-Based AR
Micro-projectors project images onto a translucent surface in front of the eye. More affordable, but larger; primarily used in early AR products.
Spatial Awareness Sensor Technology
AR smart glasses rely on sensors to understand the user's surroundings and accurately overlay digital elements.
Cameras
RGB cameras capture the real environment for mixed reality visuals.
Depth cameras (time-of-flight or structured light) measure distance and support gesture tracking.
IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units)
Combines accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers to track head orientation and movement.
2.3 GPS and Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM)
GPS provides outdoor location data, while SLAM builds real-time 3D maps indoors, enabling accurate AR object positioning.
Processing Chips and Performance
Behind the scenes, powerful processors and AI chips drive real-time rendering and sensor fusion:
Dedicated AR SoCs: Qualcomm Snapdragon XR2 Gen 2 and MediaTek Dimensity XR chips handle AR graphics processing and 6DoF tracking. AI Accelerator: Enables on-device speech recognition, image classification, and contextual assistance without constant cloud reliance.
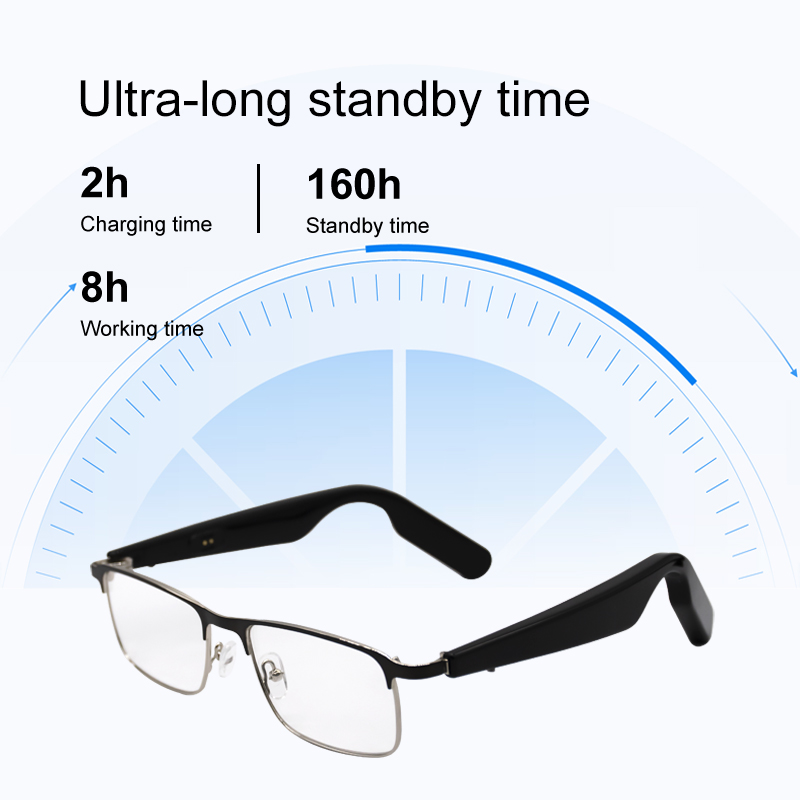
Power Consumption: Modern chips offer a balance between performance and battery life, enabling 4-8 hours of continuous AR use.
Interaction: Hands-free and Intuitive: AR smart glasses are designed for natural, hands-free interaction, allowing users to focus on their surroundings.
Voice Control: Integrated AI assistants (Google, Alexa, Meta AI) support commands like "take a photo" or "show my schedule."
Gesture Control: The camera or infrared sensor detects hand movements (e.g., pinch-to-select, swipe-to-navigate).
Enterprise-grade models are suitable for sterile or hands-on environments.
Touch Bezel: The side panel acts as a touchpad; tap or swipe to adjust volume, switch apps, or take a photo.
Eye Tracking: Advanced models track gaze direction for precise menu selection and foveated rendering (high-resolution rendering of the point you're looking at).
Power and Connectivity
Battery System: Compact lithium-polymer battery, typically integrated into the temple; some models use a charging case for extended battery life.
Connectivity: Bluetooth 5.3, Wi-Fi 6/6E, and an optional 5G module for cloud-based AR experiences.
Low-latency streaming: A must-have for gaming and remote work scenarios.
Understanding Why the Technology Matters
Understanding how AR smart glasses work can help buyers set realistic expectations:

Lightweight designs typically favor waveguides and AI-powered audio for everyday wear.
Enterprise-grade models add depth sensors and 6DoF tracking for industrial applications.
The right choice depends on the use case (entertainment, work, travel) and budget.
Future Outlook
By 2027, we expect to see more compact optical systems, higher-resolution microdisplays, and on-device AI that can predict user intent. Gesture-free interaction (eye contact and voice only) and affordable consumer AR smart glasses priced under $300 are likely to become mainstream.